Course Name: Algorithmic Problem Solving
Course Code: 23ECSE309
Name: Vineet Pai
SRN: 01FE21BCS273
University: KLE Technological University, Hubballi-31
Portfolio domain: Video streaming platform Portfolio
Introduction
The first websites were simple pages of text with maybe an image or two. Today, however, anyone with a fast enough Internet connection can watch high-definition movies or make a video call over the Internet. This is possible because of a technology called streaming.
Streaming is the continuous transmission of audio or video files from a server to a client. In simpler terms, streaming is what happens when consumers watch TV or listen to podcasts on Internet-connected devices. With streaming, the media file being played on the client device is stored remotely, and is transmitted a few seconds at a time over the Internet.[1]
Why this Portfolio?
Video streaming is becoming extreamly popular nowdays and there is no fall in watch time in near future, todays kids are getting addicted to youtube videos, shorts, tiktok, insta reels etc. All of it containing videos at core. 80% of internet by size is video content and on average 17 hours of video is streamed every week by an internet user [2]. I personally use stream youtube videos 2-3 hours per day. For businesses, the potential to reach consumers via online videos is high.
Objectives
Identifing functions and features for a Video streaming platform.
To improvise and implementation of functions using algorithms and data structures.
Improve the overall user interface and experience to ensure a smooth and engaging streaming journey.
Business use cases
1] Loading video
For a user to watch/stream video on his favorite platform his device needs to load that video from the platforms servers where it is stored.
Watching can be done is two ways
- download whole video
- load in parts(streaming)
Downloading the whole video has several disadvantages:
- User has to wait until the entire video is downloaded.
- User cannot switch between different video quality options.
- If the user loses interest midway, the downloaded parts go unused.
- Takes up space on the user’s device; some videos can be hours long and several GBs in size. Hence streaming is better than downloading whole video.
Measures to make streaming better
Video transcoding
It is the process of converting a video file from one format to another. This involves decoding the original video file into an uncompressed format and then re-encoding it into the desired format. In this process metadata like thumbnail, title, description can also be embeded.
 [4]
[4]
- Benefits of video transcoding:
- Compatibility: Ensures videos can be played on various devices and platforms by converting to supported formats.
- Streaming Efficiency: Facilitates adaptive bitrate streaming, providing multiple quality options based on the viewer’s internet connection and device capabilities.
- Storage Optimization: Compresses video files to reduce their size, making storage more efficient and cost-effective.
- Broad Accessibility: Makes content accessible to a wider audience by ensuring it can be viewed on different devices with varying technical specifications.
- Content Delivery: Improves content delivery networks (CDNs) efficiency by providing optimized video formats for faster and more reliable distribution.
Design techniques and Algorithms for Transcoding
Huffman coding
It is an efficient method for data compression, minimizes total number of bits used to represent a set of data. It is a lossless compression technique, it creates a min-heap of characters based on there frequency in data.
Time Complexity: O(nlog(n)), n=number of unique characters
Space Complexity: O(n)
Implementation of Huffman code[5]
H264
Also known as Advanced Video Coding (AVC), is a popular video compression standard used for compression and distribution of videos, it offers high compression efficiency, which reduced the bandwidth required for video streaming.
Encoding Complexity: O(nlog(n)), n is number of pixels in a frame
Implementation of H264[6]
2] Use of CDNs
Content delivery networks are servers which stores the content near to users, hence reducing time required to load video. If a video resides in a server at palo alto, a CDN in mumbai will cache that video so whenever that video is accessed by any user in India, CDN will provide it.
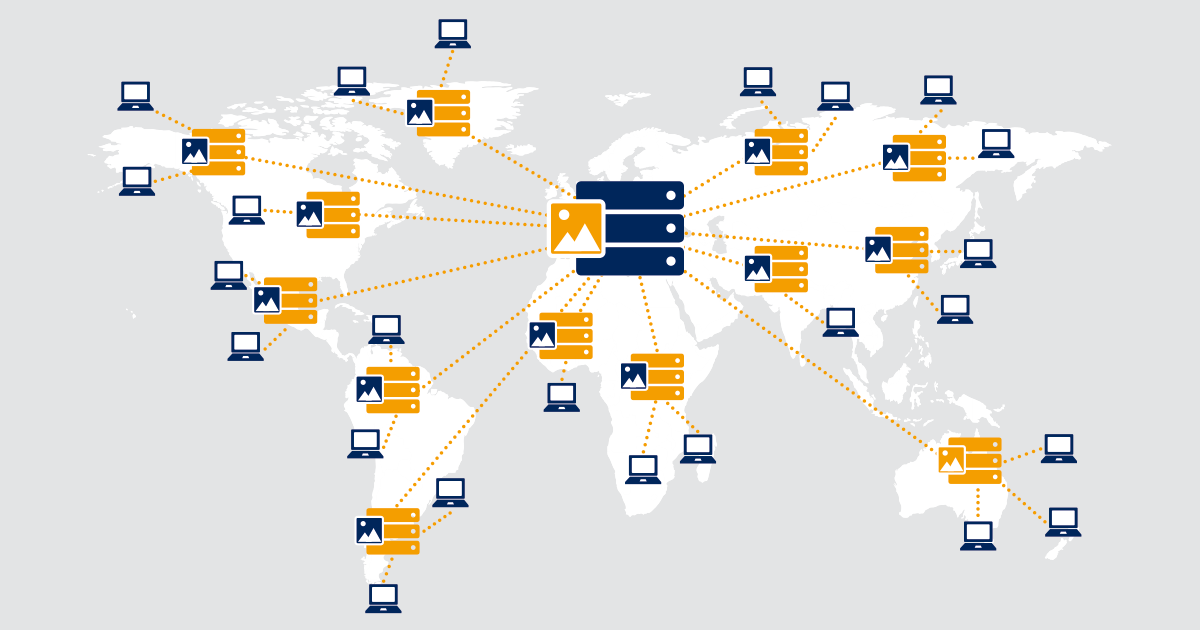 [7]
[7]
Challenges: finding nearest CDN
Design techniques and Algorithms
Dijkstra’s algorithm
If a network of CDN servers was created than Dijkstra’s can be employed to get shortest path between client and them.
Technique: Greedy approach, single source shortest path.
Time Complexity: O((V + E) log V), where V is the number of vertices and E is the number of edges.
Space Complexity: O(V), due to the storage requirements for the distance array and the set of visited nodes.
Implementation of Dijkstra algo[8]
A* search
A* Search Algorithm: Greedy approach, heuristic based
Time Complexity: O(E), where E is the number of edges in the graph.
Space Complexity: O(V) auxiliary space in worst case.
Implementation of A* algo[9]
3] Creating topic domains
Topic domains are groups of related or identical videos organized into a hierarchical structure based on specific topics such as gaming, education, films, music, etc. Each domain can contain sub-domains and sub-sub-domains, creating a multi-level hierarchy.
[10]
- Benefits:
- Targeted Changes: If the platform needs to make changes to specific videos, the hierarchical structure allows for targeted modifications within a particular domain or sub-domain.
- Improved Recommendations: When users frequently watch videos from two different domains, the platform can recommend these videos to other users, enhancing the recommendation system.
- Challenges:
- Classification accuracy
- Handling continuous addition of new videos
Design techniques and Algorithms:
Graphs
Graphs are data structures consisting of nodes (vertices) and edges that connect pairs of nodes, used to represent relationships between entities.
Nodes: Represent videos.
Edges: Represent relationships between videos.
Hierarchical Structure: Represented using parent-child relationships within the graph.
Time complexity: O(1) for adding node.
Space complexity: O(V + E) where V is the number of videos (nodes) and E is the number of relationships (edges)
Implementation of graph[11]
4] Playing video
While playing videos, segments need to be dynamically loaded from servers or CDNs. Users often switch between different sections of the video, requiring an efficient method to prioritize which segments to load. Using a heap with priority can help in selecting which segments to load based on various criteria such as chapters created by the artist, most viewed sections, and segments frequently jumped to by viewers.
 [12]
[12]
- Benefits:
- Saving Time: Ensures quick access to important segments.
- Efficient Use of Bandwidth: Prioritizes loading of segments that are more likely to be viewed.
- Improved User Experience: Ensures that the most important segments are loaded first, reducing buffering time.
Design techniques and Algorithms:
Heap
A specialized binary tree-based data structure that satisfies the heap property: in a max heap, each parent node is greater than or equal to its children, and in a min heap, each parent node is less than or equal to its children.
Time complexity: O(log(n)) for getting next segment.
Space complexity: O(n)
Implementation of heap[13]
5] Search results
Searching is one of the main feature of an video streaming platform. When user want to watch a specific video he/she searches for specific key word in the search bar. Platform should show results related to those key words.
- Benefits:
- Specific search results leads to more user inflow
Design techniques and Algorithms:
Boyer Moore Algorithm
It starts matching from the last character of the search word with video title given by creator.
Time complexity: O(n * m), n = size of keyword, m=size of title
Space complexity: O(n + m)
Implementation of Boyer moore[14]
Trie, heuristic-based
Time Complexity: O(n) for insertion and searching where n is the length of the string.
Space Complexity: O(n*avgm) where n is the number of words and avgm is the average length of the words.
Implementation of trie[16]
6] Autocompletion of search
Autocompletion are suggestions provided by platform to help users refine or expand their search queries. These recommendations are typically based on popular searches, user’s previous searches, and algorithms designed to predict what the user might be looking for.
[15]
Trie data structure can be employed for this task.
- Benefits:
- Guiding user to more accurate results.
- Improves search efficiency.
Design techniques and Algorithms:
Trie, heuristic-based
Time Complexity: O(n) for insertion and searching where n is the length of the string.
Space Complexity: O(n*avgm) where n is the number of words and avgm is the average length of the words.
Implementation of trie[16]
7] Autocorrection of search
Auto-correction in search helps users find the content they are looking for even if they make typographical errors or misspell words. This feature improves the search experience by suggesting correct or alternative queries, thereby increasing the chances of finding relevant results.
- Benefits:
- Guiding user to more accurate results.
- Improves search accuracy and relevance.
Design techniques and Algorithms:
Trie
Time Complexity: O(n) for insertion and searching where n is the length of the string.
Space Complexity: O(n*avgm) where n is the number of words and avgm is the average length of the words.
Implementation of trie[16]
Levenshtein Distance
Levenshtein distance is a measure of the similarity between two strings, which takes into account the number of insertion, deletion and substitution operations needed to transform one string into the other.
Time Complexity: O(mxn)
Space Complexity: O(mxn)
m, n are key and title.
Implementation[17]
Hamming distance
It can only be applied to strings of equal length, it is used measures the number of positions at which the corresponding characters are different.
Time Complexity: O(n) n = length of string
Space Complexity: O(1) variable to store diffrence.
Implementation of Hamming distance[18]
8] Subscription
User to be allowed to subscribe to their favorite creator, so that a priority can be set by platform that enables user to watch latest videos by favorite creator at earliest
- Benefits:
- A moral support to creators
- Advertisement agencies can use this matric for payments
- Less distraction to users.
Challenges:
Dynamic in nature.
large in number.
Design techniques and Algorithms:
Hash maps
It is a dictionary of channels subscribed by user. It achieves efficient lookups, insertions, and deletions by using a hash function to compute an index into an array of buckets or slots.
Time Complexity: O(n) n = number of keys stored.
Space Complexity: O(n) n = number of key value pairs stored.
Implementation of hash maps[19]
9] Maintaining history
Previously watched videos can be stored to establish connections and relations in the topic domains that is previously created. Lazy propagation can be used to update these when the server load was less.
- Benefits:
- User can track his activity
- Platform can use this data to improvise on recommendations.
Challenges:
History may be very large.
Design techniques and Algorithms:
Doubly linked list
Tt can be employed for easy switching between videos.
Time Complexity: O(n)
Space Complexity: O(n)
n = number of videos stored.
10] Watch later
The “Watch Later” feature allows users to save videos they come across while browsing the platform, enabling them to easily find and watch these videos at a later time. This enhances the user experience by providing a convenient way to bookmark interesting content.
- Benefits:
- User convenience
- Increased engagement
Design techniques and Algorithms:
Queue
Time Complexity: O(1) to access and insert.
Space Complexity: O(n)
n = number of videos stored.
11] Time based stats
When a creator uploads a video, timing is one of the most important things to bother about. Videos uploaded at 3am may not get as much views as video uploaded at 8pm. Likes and comments on a video can be taken as time series data on which severals operations can be made to get valuable insights.
- Benefits:
- Based on number of comments and likes, creator can choose a time range in between to upload next video.
- Creator can track video reach.
Design techniques and Algorithms:
Segment tree
[20]
Time Complexity: O(n) to build, O(log(n)) for query.
Space Complexity: O(n)
Implementation of segment tree[21]
12] Video recommendations
Videos can be recommended to users based on their previous watches or the user with whom their taste matches. This can be found our by channel subscription, liking a video, positive commenting on videos, sharing videos etc. ALS(alternating least square) can be used for filtering similarities.
Design techniques and Algorithms:
ALS Algorithm
Time Complexity: O(U x I^2) where U and I represent the total number of Users and Items.
Space Complexity: O(U*I) for the 2D matrix
Implementation of ALS algo[22]
13] Traffic management
Routing the data to the user may have several ways. Platform can preconfigure the routes based on bandwidth and traffic in a specific area. Graph algorithms like Ford-fulkerson can help in reducing congestion.
- Benefits:
- Scalability
- Cost savings
- Low latency.
Design techniques and Algorithms:
Max flow algorithm - Ford Fulkerson
[23]
Time Complexity: O(V*E^2)
where E is the number of edges and V is the number of vertices of the graph.
Space Complexity: O(V) for queue.
Implementation of Ford fulkerson[24]
14] Traffic source
Views from developed countries typically generate higher ad revenue due to larger advertiser budgets and higher ad rates. This leads to more lucrative sponsorship opportunities and premium ad placements for videos attracting viewers from these regions.
[25]
- Benefits
- Platform can make better decision on monetaization.
- Creators can tune their content and language of choice.
Challenges:
Large amount of data
Design techniques and Algorithms:
Dictornay data structure
for a single channle a dictonary can be maintained containing video number, country wise view count and other data.
Time Complexity: O(1) almost nil for creation and query.
Space Complexity: O(n) based on number of videos.
15] Handling hate speech and abuse
Videos have comments sections for user engagement and opinion sharing. But regulating these comments is very much needed to avoid hate speech and communal clashes in the society.[3] This can be done using simple algorithms or NLP and deep learning algorithms.
[26]
- Benefits
- Maintaines platform guidlines.
- Creator abuse is avoided.
Challenges:
Large amount of data.
New words of abuse in market.
Design techniques and Algorithms:
Rabin karp algorithm (hashing)
The Rabin-Karp algorithm is a string-searching algorithm that uses hashing to find an occurrence of a “pattern” string within a “text” string.
Time Complexity: O(mxn) worst case, n and m are size of comment and keyword.
Space Complexity: O(1)
Implementation of Rabin karp[27]
16] CDN requests balancing
In scenarios where a single server must handle several thousand clients, each potentially making multiple requests, deciding the order in which to serve clients becomes crucial. Several scheduling algorithms can be employed to manage this situation effectively. Each algorithm has its advantages and is suited for different types of applications and requirements.
[28]
- Challenges:
- large number of clients requesting simulatinously.
- limited number of servers.
- Benefits:
- Satisfied customers.
- low capital investment.
Design techniques and Algorithms:
Round robin
Each request is given a fixed time slice or quantum, and requests are cycled through in a circular queue.
Weighted Fair Queuing (WFQ)
 Each request or client is assigned a weight, and service is distributed based on these weights.
Each request or client is assigned a weight, and service is distributed based on these weights.
Platform can weight premium customer high, so that they can be served better.
Learning
I have learnt a lot from this portfolio. Designing a platform for video streaming which probably used by billions is fascinating to me. I personally stream videos over youtube for hours a day, this portfolio project made me think how the all these things work in the backend. How modern algorithms and data structures can make platforms like these efficient and user friendly, how this affects the life of billions. This project will be helpful to those who would like to build a portfolio like these.
References
[1] Cloudflare. (n.d.). What is streaming? Cloudflare Learning. Available: https://www.cloudflare.com/learning/video/what-is-streaming/ [Accessed: July 8, 2024].
[2] Oberlo. (n.d.). Online video consumption statistics. Oberlo. Available: https://www.oberlo.com/statistics/online-video-consumption-statistics [Accessed: July 8, 2024].
[3]ResearchGate. (n.d.). Architecture of video transcoding. ResearchGate. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/257879554/figure/fig2/AS:267897603883015@1440883174034/Architecture-of-video-transcoding.png [Accessed: July 8, 2024].
[4]R. Rejaie, M. Handley, and D. Estrin, “Architectural Video Transcoding,” presented at the Proceedings of the 9th International Workshop on Network and Operating Systems Support for Digital Audio and Video (NOSSDAV ‘99), 1999. [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/257879554/figure/fig2/AS:267897603883015@1440883174034/Architecture-of-video-transcoding. [Accessed: Jul. 8, 2024].
[5]Elzawawy. (n.d.). Huffman Coding Zipper. GitHub. Available: https://github.com/Elzawawy/huffman-coding-zipper [Accessed: July 8, 2024].
[6]Cisco. (n.d.). OpenH264. GitHub. Available: https://github.com/cisco/openh264?tab=readme-ov-file [Accessed: July 8, 2024].
[7]Paessler AG. (n.d.). CDN orange. Paessler Blog. Available: https://blog.paessler.com/hubfs/cdn-orange.png [Accessed: July 8, 2024].
[8]M. Burst. (n.d.). Dijkstra’s Algorithm. GitHub. Available: https://github.com/mburst/dijkstras-algorithm [Accessed: July 8, 2024].
[9]E. Ueland. (n.d.). Astar-Algorithm. GitHub. Available: https://github.com/EinarUeland/Astar-Algorithm [Accessed: July 8, 2024].
[10]M. Alfano. (n.d.). Network of the top semantic tags on NPRs The Two Way news section. ResearchGate. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Mark-Alfano/publication/329819896/figure/fig2/AS:729429030473728@1550920841314/Figure-Network-of-the-top-semantic-tags-on-NPRs-The-Two-Way-news-section-in.ppm [Accessed: July 8, 2024].
[11]Y. Barninets. (n.d.). Graph. GitHub. Available: https://github.com/YuriiBarninets/graph [Accessed: July 8, 2024].
[12]YouTube. (n.d.). Maxresdefault.jpg. YouTube. Available: https://i.ytimg.com/vi/3Wt03kC-34I/maxresdefault.jpg [Accessed: July 8, 2024].
[13] GeeksforGeeks. (n.d.). Heap Implementation in Java. GeeksforGeeks. Available: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/heap-implementation-in-java/ [Accessed: July 8, 2024].
[14]GeeksforGeeks. (n.d.). Boyer-Moore Algorithm for Pattern Searching. GeeksforGeeks. Available: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/boyer-moore-algorithm-for-pattern-searching/ [Accessed: July 8, 2024].
[15]Microsoft. (n.d.). Image. Bing. Available: https://th.bing.com/th/id/OIP.t11GPQSMJ5pMd6tk0GSkEQHaDt?w=314&h=174&c=7&r=0&o=5&pid=1.7 [Accessed: July 8, 2024].
[16]GeeksforGeeks. (n.d.). Trie | Insert and Search. GeeksforGeeks. Available: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/trie-insert-and-search/ [Accessed: July 8, 2024].
[17]GeeksforGeeks. (n.d.). Introduction to Levenshtein Distance. GeeksforGeeks. Available: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/introduction-to-levenshtein-distance/ [Accessed: July 8, 2024].
[18]GeeksforGeeks. (n.d.). Hamming Distance between two strings. GeeksforGeeks. Available: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/hamming-distance-two-strings/ [Accessed: July 8, 2024].
[19]GeeksforGeeks. (n.d.). Java.util.HashMap in Java with Examples. GeeksforGeeks. Available: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/java-util-hashmap-in-java-with-examples/ [Accessed: July 8, 2024].
[20]Microsoft. (n.d.). Image. Bing. Available: https://th.bing.com/th/id/OIP.mKHmJcTtsxjmqYGgL9MVXwHaFz?w=199&h=180&c=7&r=0&o=5&pid=1.7 [Accessed: July 8, 2024].
[21]Ouuan. (n.d.). SegmentTree. GitHub. Available: https://github.com/ouuan/segmentTree [Accessed: July 8, 2024].
[22]Yeomko22. (n.d.). ALS_implementation. GitHub. Available: https://github.com/yeomko22/ALS_implementation [Accessed: July 8, 2024].
[23]Microsoft. (n.d.). Image. Bing. Available: https://th.bing.com/th/id/OIP.knzFHUlyuCHGtc-qMzHfNQHaEX?w=275&h=180&c=7&r=0&o=5&pid=1.7 [Accessed: July 8, 2024].
[24]GeeksforGeeks. (n.d.). Ford-Fulkerson Algorithm for Maximum Flow Problem. GeeksforGeeks. Available: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/ford-fulkerson-algorithm-for-maximum-flow-problem/ [Accessed: July 8, 2024].
[25]Microsoft. (n.d.). Image. Bing. Available: https://th.bing.com/th/id/OIP.RKRsqO8wG7VP_bZCSF-p-gHaFC?w=203&h=180&c=7&r=0&o=5&pid=1.7 [Accessed: July 8, 2024].
[26]Microsoft. (n.d.). Image. Bing. Available: https://th.bing.com/th/id/OIP.WBPOFMXcs3NXUWF2E1UD4wAAAA?w=225&h=180&c=7&r=0&o=5&pid=1.7 [Accessed: July 8, 2024].
[27]GeeksforGeeks. (n.d.). Rabin-Karp Algorithm for Pattern Searching. GeeksforGeeks. Available: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/rabin-karp-algorithm-for-pattern-searching/ [Accessed: July 8, 2024].
[28]Microsoft. (n.d.). Image. Bing. Available: https://th.bing.com/th/id/OIP.kwegEO5YJg9N_G_o0RNPuQHaEA?w=334&h=180&c=7&r=0&o=5&pid=1.7 [Accessed: July 8, 2024].